Abstract
Introduction
Hemophilia patients and providers have more treatment options than ever before. Integration of extended half-life (EHL) factor products into routine use for hemophilia A or B prophylaxis varies across hemophilia treatment centers (HTCs) and has not been formally described. The ATHNdataset is a national database of bleeding disorder and thrombosis patients who opt-in from 138 ATHN-affiliated HTCs and includes required core data elements. The primary aim of this longitudinal, observational study is to characterize the evolving real-world use of factor VIII (FVIII) and factor IX (FIX) concentrates, including rate of switching from one factor replacement product to another (switch rate), comparative annual factor consumption, and infusion frequency using serial queries of the ATHNdataset. A sub-study of detailed site-level questionnaires, above and beyond the ATHNdataset, including 8 HTCs evaluated the ability of the ATHNdataset to capture changes in EHL product use in real-time and demonstrate the fidelity of the ATHNdataset.
Methods
All patient level data was collected and analyzed under the patient authorization for the ATHNdataset. The selected population for analysis included all patients with moderate and severe hemophilia A or B without active inhibitors. EHL products were defined as those with moieties added with intention of half-life extension. The ATHNdataset was queried at baseline (June 2016) and follow-up 9 months later (March 2017). Sub-study site-level switching data was captured via quarterly RedCap™ questionnaires.
Results
ATHNdataset analysis
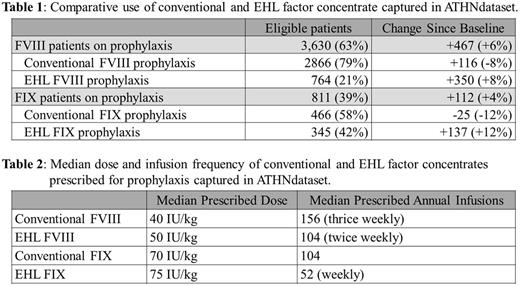
At baseline, 7,552 patients were analyzed (5,504 FVIII, 1978 FIX). Of 3,163 FVIII patients on prophylaxis 87% were prescribed conventional FVIII concentrates and 13% EHL concentrates. Of the 699 FIX patients on prophylaxis 70% were prescribed conventional FIX concentrates, 30% EHL concentrates. Median dose and infusion frequency for FVIII products were 40 IU/kg/dose and 156 annual infusions and for FIX were 65 IU/kg/dose and 104 annual infusions.
The 9-month follow-up analysis yielded 7,864 patients eligible (5,764 FVIII, 2,100 FIX). Frequency of use for both EHL FVIII and FIX is increasing. Baseline use of EHL FIX was substantially higher than that of EHL FVIII and continues to rise. Growth in use of EHL FVIII for prophylaxis was 3 times that of conventional FVIII. In aggregate 17% of patients changed from an on-demand to prophylaxis regimen with 40% of these patients initiating prophylaxis with an EHL product.
Table 1: Comparative use of conventional and EHL factor concentrate captured in ATHNdataset.
Table 2: Median dose and infusion frequency of conventional and EHL factor concentrates prescribed for prophylaxis.
Sub-study analysis
Eight sites representing 1009 patients with moderate and severe hemophilia A or B from across the U.S. participated in the sub-study analysis. At baseline 8% of these patients were prescribed EHL concentrates. Across sites, the median was 10 patients (range: 0-18). Of the patients on an EHL product participating in the ATHNdataset, 63% were on EHL FVIII. At the 9-month follow-up an additional 33 patients had switched to an EHL product (17 FVIII, 16 FIX) equating to an overall EHL use of only 11.6%. Two patients switched among EHL products and 2 returned to a conventional product. Half of sub-study sites reported routinely obtained blood samples for PK analysis; 6 of 8 sites reported obtaining blood samples for PK analysis for patient switching to EHL products during follow-up period.
Conclusion
The ATHNdataset presents a unique opportunity to investigate practice changes among U.S. HTCs. Uptake of EHL FVIII has been modest despite the first product being licensed in 2014. In contrast, the use of EHL FIX has now risen to greater than 40% of patients receiving prophylaxis. The median usage of EHL FVIII results in 27% reduction of annual units of factor prescribed for prophylaxis, and 46% reduction for EHL FIX compared to conventional products. The incremental increase in per unit price of EHL products, 30-72% greater than conventional products, exceeds the annual reduction of product usage. Consistent reporting of bleed events and adherence are not currently available for comparison. The contrast between sub-study uptake results and the ATHNdataset results highlight the practice variability among HTCs with respect to integration of EHL products into clinical care.
Croteau: ATHN/Hemophilia of Georgia: Research Funding; Octapharma: Honoraria; Baxalta, Dimension Therapeutics, Genentech, Pfizer: Research Funding; Aptevo, Baxalta/Shire, Bayer, CSL Behring, Genentech, Novo Nordisk, Octapharma, Pfizer: Consultancy. Raffini: Green Cross Inc: Consultancy; Genetech: Consultancy; CSL Behring: Consultancy; Bayer: Consultancy. Silvey: Pfizer, CSL Behring, Octapharma: Consultancy. Wheeler: NovoNordisk: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Bayer: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Octapharma: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Shire: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Neufeld: Novartis: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Genentech: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Octapharma: Consultancy, Honoraria.
Author notes
Asterisk with author names denotes non-ASH members.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal